JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)是一种比XML更轻量级的数据交换格式,在易于人们阅读和编写的同时,也易于程序解析和生成。尽管JSON是JavaScript的一个子集,但JSON采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式,且表现为键/值对集合的文本描述形式(类似一些编程语言中的字典结构),这使它成为较为理想的、跨平台、跨语言的数据交换语言。

开发者可以用 JSON 传输简单的字符串、数字、布尔值,也可以传输一个数组,或者一个更复杂的复合结构。在 Web 开发领域中, JSON被广泛应用于 Web 服务端程序和客户端之间的数据通信。
Go语言内建对JSON的支持。使用Go语言内置的encoding/json 标准库,开发者可以轻松使用Go程序生成和解析JSON格式的数据。
JSON官方网站:http://www.json.org/
在线格式化:http://www.json.cn/
10.3.1 编码JSON
10.3.1.1 通过结构体生成JSON
使用json.Marshal()函数可以对一组数据进行JSON格式的编码。
json.Marshal()函数的声明如下:
func Marshal(v interface{}) ([]byte, error)
还有一个格式化输出:
// MarshalIndent 很像 Marshal,只是用缩进对输出进行格式化func MarshalIndent(v interface{}, prefix, indent string) ([]byte, error)
1) 编码JSON
示例代码:
package mainimport ("encoding/json""fmt")type IT struct {Company stringSubjects []stringIsOk boolPrice float64}func main() {t1 := IT{"itcast", []string{"Go", "C++", "Python", "Test"}, true, 666.666}//生成一段JSON格式的文本//如果编码成功, err 将赋于零值 nil,变量b 将会是一个进行JSON格式化之后的[]byte类型//b, err := json.Marshal(t1)//输出结果:{"Company":"itcast","Subjects":["Go","C++","Python","Test"],"IsOk":true,"Price":666.666}b, err := json.MarshalIndent(t1, "", " ")/*输出结果:{"Company": "itcast","Subjects": ["Go","C++","Python","Test"],"IsOk": true,"Price": 666.666}*/if err != nil {fmt.Println("json err:", err)}fmt.Println(string(b))}
2) struct tag
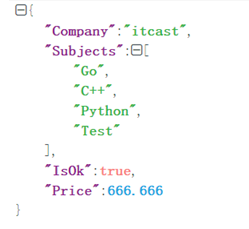
我们看到上面的输出字段名的首字母都是大写的,如果你想用小写的首字母怎么办呢?把结构体的字段名改成首字母小写的?JSON输出的时候必须注意,只有导出的字段(首字母是大写)才会被输出,如果修改字段名,那么就会发现什么都不会输出,所以必须通过struct tag定义来实现。
针对JSON的输出,我们在定义struct tag的时候需要注意的几点是:
- 字段的tag是”-“,那么这个字段不会输出到JSON
- tag中带有自定义名称,那么这个自定义名称会出现在JSON的字段名中
- tag中如果带有”omitempty”选项,那么如果该字段值为空,就不会输出到JSON串中
- 如果字段类型是bool, string, int, int64等,而tag中带有”,string”选项,那么这个字段在输出到JSON的时候会把该字段对应的值转换成JSON字符串
示例代码:
type IT struct {//Company不会导出到JSON中Company string `json:"-"`// Subjects 的值会进行二次JSON编码Subjects []string `json:"subjects"`//转换为字符串,再输出IsOk bool `json:",string"`// 如果 Price 为空,则不输出到JSON串中Price float64 `json:"price, omitempty"`}func main() {t1 := IT{Company: "itcast", Subjects: []string{"Go", "C++", "Python", "Test"}, IsOk: true}b, err := json.Marshal(t1)//json.MarshalIndent(t1, "", " ")if err != nil {fmt.Println("json err:", err)}fmt.Println(string(b))//输出结果:{"subjects":["Go","C++","Python","Test"],"IsOk":"true","price":0}}
10.3.1.2 通过map生成JSON
// 创建一个保存键值对的映射t1 := make(map[string]interface{})t1["company"] = "itcast"t1["subjects "] = []string{"Go", "C++", "Python", "Test"}t1["isok"] = truet1["price"] = 666.666b, err := json.Marshal(t1)//json.MarshalIndent(t1, "", " ")if err != nil {fmt.Println("json err:", err)}fmt.Println(string(b))//输出结果:{"company":"itcast","isok":true,"price":666.666,"subjects ":["Go","C++","Python","Test"]}
10.3.2 解码JSON
可以使用json.Unmarshal()函数将JSON格式的文本解码为Go里面预期的数据结构。
json.Unmarshal()函数的原型如下:
func Unmarshal(data []byte, v interface{}) error
该函数的第一个参数是输入,即JSON格式的文本(比特序列),第二个参数表示目标输出容器,用于存放解码后的值。
10.3.2.1 解析到结构体
type IT struct {Company string `json:"company"`Subjects []string `json:"subjects"`IsOk bool `json:"isok"`Price float64 `json:"price"`}func main() {b := []byte(`{"company": "itcast","subjects": ["Go","C++","Python","Test"],"isok": true,"price": 666.666}`)var t ITerr := json.Unmarshal(b, &t)if err != nil {fmt.Println("json err:", err)}fmt.Println(t)//运行结果:{itcast [Go C++ Python Test] true 666.666}//只想要Subjects字段type IT2 struct {Subjects []string `json:"subjects"`}var t2 IT2err = json.Unmarshal(b, &t2)if err != nil {fmt.Println("json err:", err)}fmt.Println(t2)//运行结果:{[Go C++ Python Test]}}
10.3.2.2 解析到interface
示例代码:
func main() {b := []byte(`{"company": "itcast","subjects": ["Go","C++","Python","Test"],"isok": true,"price": 666.666}`)var t interface{}err := json.Unmarshal(b, &t)if err != nil {fmt.Println("json err:", err)}fmt.Println(t)//使用断言判断类型m := t.(map[string]interface{})for k, v := range m {switch vv := v.(type) {case string:fmt.Println(k, "is string", vv)case int:fmt.Println(k, "is int", vv)case float64:fmt.Println(k, "is float64", vv)case bool:fmt.Println(k, "is bool", vv)case []interface{}:fmt.Println(k, "is an array:")for i, u := range vv {fmt.Println(i, u)}default:fmt.Println(k, "is of a type I don't know how to handle")}}}
更新时间:2018-06-18 06:39
